What is NDPR?
Allow me to paint a scenario, imagine attending a vibrant Nigerian wedding, the air alive with the rustle of colorful Aso Ebi and the joyous chatter of guests. Each intricate pattern on the fabric tells a story, unique to the wearer. Let's bring to the case of NDPR, but what if, instead of threads, these patterns were made of personal data – your name, address, secret websites, your card details, online habits, even your deepest desires?
Would you wear it with pride, or fear its exposure?
This is the delicate dance at the heart of the Nigeria Data Protection Regulation (NDPR), a legal framework aiming to safeguard the privacy of Nigerians in the digital age. Enacted in 2019, the NDPR has woven a new thread into the fabric of Nigerian society, one that empowers individuals and holds organizations accountable for handling their data responsibly.
The objectives of the regulation are as follows:
▪ to safeguard the rights of natural persons to data privacy;
▪ to foster safe conduct for transactions involving the exchange of
Personal Data;
▪ to prevent manipulation of Personal Data and
▪ to ensure that Nigerian businesses remain competitive in international trade through the safe-guards afforded by a sound data protection regulation.
The regulation applies to all storage and processing of Personal Data conducted in respect of Nigerian citizens and residents.
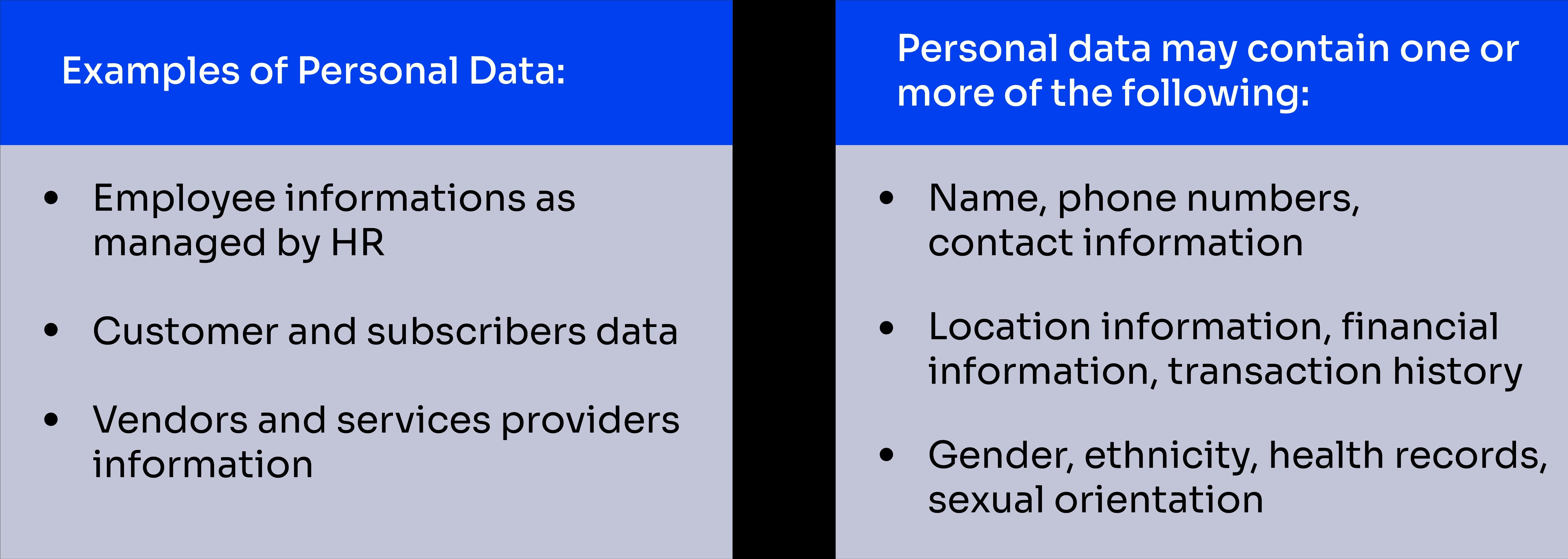
Compliance Requirements:
The NDPR regulation requires that Data Controllers and Data Processors:
-Engage a Data Protection Compliance Organization (DPCO) to perform a Data Protection Audit and file a report with NITDA within the stipulated timeline.
-Designate a Data Protection Officer (DPO) who will be responsible for driving NDPR compliance initiatives within the organization.
-Document and publish a data protection policy in line with the requirements of the Data Protection Regulation.
-Ensure continuous capacity building and training for Data Protection Officer and other personnel involved
in processing personal data.
Consequences for Non-compliance
-Maximum penalty for breaches of data privacy rights on international transfers can be up to N10M or 2% of annual gross revenue of the preceding year, whichever is greater and based on the number of Data Subjects dealt with.
-Reputational Damage
Negative publicity and damage to brand and reputation.
-Prosecution
Prosecution of principal officers in the event of a severe data breach.
Stats that speak volumes:
* Since its implementation, NITDA has received over 2,000 inquiries and complaints related to data protection, highlighting the growing awareness and engagement with the NDPR. (Source: NITDA Annual Report 2021)
* A 2022 survey by DataPro Nigeria revealed that 72% of Nigerian businesses had implemented measures to comply with the NDPR, showcasing a positive shift towards data protection awareness. (Source: DataPro Nigeria 2022 Data Protection Compliance Survey)
Conclusion
The NDPR's impact goes beyond statistics. It's about weaving a culture of data privacy into the Nigerian fabric, one where individuals feel empowered and organizations act responsibly. As technology continues to evolve, the NDPR will likely need to adapt, but its core principles – transparency, accountability, and respect for privacy – remain timeless, ensuring that in the digital age, our personal data remains as uniquely protected as the intricate patterns of an Aso Ebi.
Read more about the NDPR here.

